
A string is a sequence of characters. The Python string data type is used to represent these sequences of characters (text). Python strings can contain letters (alphabet), numbers, and symbols. Python Strings are enclosed in single ('...'), double ("...") or triple ("""....""", ‘''...''') quotations.
Table of Contents
Create String Variable and Assign Value
We assign a string or set of text to a variable in Python, by simply writing the name of the variable, and then using an equal sign (=), and finally, put the string value.
The string value in Python can be defended using any of the following options:
Singleline String Value
The Singleline String Values are defined by enclosing the string values in either a double quote ("...") or a single quote ('...').
Example:
# Create Python variable and store with string value
# Use double quate
var_str1 = "This is a String used with double quotation"
# Use single quate
var_str2 = 'This is a String used with single quotation'
# Display the string literals using print() function in python
print(var_str1)
print(var_str2)
print("I like Python Strings")
Output:
This is a String used with double quotation
This is a String used with single quotation
I like Python Strings
Multiline String Value
The Multiline String Values are defined by enclosing the string values in either triple-double quotes ("""...""") or triple-single quotes ('''...''').
Multiline Strings Values can span across multiple lines and can contain line breaks (new lines) and other special characters. n Python, this means that when line breaks or new lines are used in a multiline string value, the string will appear in the same position as they are in the code.
Example:
# Create a variable and assign a multiline string value in Python
# We use triple double qoatation
var_multiline_str1 = """Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet,
consectetur adipiscing elit,
sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt
ut labore et dolore magna aliqua."""
# you can also use a triple single quates
var_multiline_str2 = '''Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet,
consectetur adipiscing elit,
sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt
ut labore et dolore magna aliqua.'''
#the above string was surrounded by three quotes otherwise it will not accept
""" normally strings are surrounded with single and double quatation, however, strings can grow beyond few words
and might become multiline, tabs and with other special charecters inside.
therefore, trible quatations will be used to support string with such carecteristics.
Note: triple quatations can be single (use three single quatations) or double quates (three double quatations)
"""
print(var_multiline_str1)
print("")
print(var_multiline_str2)
Output:
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet,
consectetur adipiscing elit,
sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt
ut labore et dolore magna aliqua.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet,
consectetur adipiscing elit,
sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt
ut labore et dolore magna aliqua.
Access String Items
Accessing string items or characters can be done using indexing and slicing. Therefore, in Python, we can use square brackets [] to indicate the index number of the character(s) we want to access.
In the following subsections, we provide practical examples of how to access string items in Python using String Indexing (both positive and negative), and String Looping techniques.
String Indexing
String Indexing is a technique used to access individual characters at a specific position in the string, This can be done by using Positive Indexing and Negative Indexing.
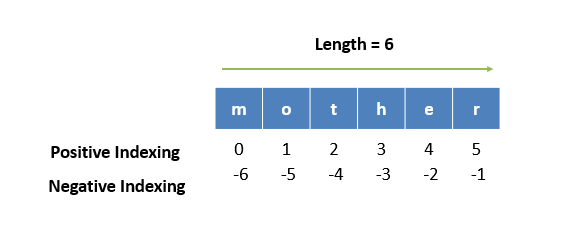
Positive Indexing: This is a technique used when accessing items in a sequence (such as strings, lists, or tuples) by using a non-negative numerical index that starts from 0 and goes up to the length of the string items minus 1.
This means, positive indexing only allows us to access the string items from left to right. While the negative numerical index starts from -1 which from right to left and goes up to the first string. This one does not apply -1 to count the length since it starts -1.
Example:
# String Indexing
# Acess string items using their index (Positive Indexing) in Python
var_str = "Strings are Object"
print(var_str[0])
print(var_str[3])
var_bool = True
print(var_str[var_bool])
print(var_str[0:8])
Output:
S
i
t
Strings
Negative Indexing: This is a technique used when accessing items in a sequence such as strings, by using a negative numerical index that starts from -1 and goes up to the length of the string items.
This type of indexing mainly starts from the end of the string instead of the beginning of the string.
This means, negative indexing only allows us to access the string characters from right to left.
Example:
# String Indexing
# Acess string items using their index (Negative Indexing) in Python
var_str = "Strings are Object"
print(var_str[-4])
print(var_str[-3])
print(var_str[-1:len(var_str)])
print(var_str[-6:])
print(var_str[:len(var_str)-1])
Output:
j
e
t
Object
Strings are Objec
String Looping
String looping is a way to access string characters. In this case, we can use forloop to access all the characters contained in a string.
The looping operation allows us to access one character from the string at a time and the looping process is continued until all the characters in the string are accessed.
Example:
# String Looping
# Access string items using for loop in Python
var_str = "This is Python String"
for i in var_str:
print("The string items of ", i)
Output:
The string items of : T
The string items of : h
The string items of : i
The string items of : s
The string items of :
The string items of : i
The string items of : s
The string items of :
The string items of : P
The string items of : y
The string items of : t
The string items of : h
The string items of : o
The string items of : n
The string items of :
The string items of : S
The string items of : t
The string items of : r
The string items of : i
The string items of : n
The string items of : g
An alternative way of using the for loop is to use the range() function and pass the length of the string as an argument. The len() function returns the length of the string.
Example:
# We can also use the range() function during the loop process
var_str = "Python is AMAZING"
for i in range(len(var_str)):
print("The string items of :", var_str[i])
Output:
The string items of : P
The string items of : y
The string items of : t
The string items of : h
The string items of : o
The string items of : n
The string items of :
The string items of : i
The string items of : s
The string items of :
The string items of : A
The string items of : M
The string items of : A
The string items of : Z
The string items of : I
The string items of : N
The string items of : G
Perform Operations on Strings
In Python, we perform operations on strings, such as combining two or more strings (concatenation) and also comparing strings using comparison operators.
We discuss how to combine and compare strings in the following subsections.
Combine Strings
Combine Strings: This combines two or more strings, by using the concatenation operator + or the join() method.
Combine string using concatenation operator +.
Example:
# Combine two Strings
var_str1 = "I love "
var_str2 = "Python"
var_str = var_str1 + var_str2
print(var_str)
print("Use + Operator " + "to Combine Strings")
print(var_str + " " + var_str)
Output:
I love Python
Use + Operator to Combine Strings
I love Python I love Python
Note: If you convert string numbers to other numeric types, the concatenation operator + will add the numbers instead of combining them because they are no longer strings.
Example:
# Perform Operations on Strings
var_str1 = "90"
var_str2 = "10.90"
var_str = var_str1 + var_str2
print(var_str)
print("Use + Operator " + "to Combine Strings")
print(var_str1 + " + " + var_str2 + " =", int(var_str1) + float(var_str2))
Output:
9010.90
Use + Operator to Combine Strings
90 + 10.90 = 100.9
Combine Strings: This combines two or more strings, using the join() method.
Combine string using the join() method.
Example:
# Combine two Strings using join() method
var_str1 = "I love "
var_str2 = "Python"
var_str = " ".join([var_str1, var_str2])
print("Use join() method" + "to Combine Strings")
print(var_str)
Output:
Use join() methodto Combine Strings
I love Python
Compare Strings
We compare Strings using string comparison operators such as the double equal ‘==’ and other comparison operators such as greater than '>', greater than equal '>=', less than '<', less than or equal '<=', and not equal '!='.
Note: In Python, string comparison is case-sensitive, which means, Java and java are two different words.
Example:
var_str1 = "Python is a programming language "
var_str2 = "Python is a coding language"
var_str = var_str1 == var_str2
print(var_str)
print("Python is a good language" == "Python is a good language")
Output:
False
True
The above example only considers the equality comparison '==' while in the following we consider other comparison operators.
Example:
# Compare Strings
var_str1 = "Python is a programming language "
var_str2 = "Python is a coding language"
var_str = var_str1 > var_str2
print(var_str)
print("Python is a good language" >= "Python is a good language")
print("Python" < "Python")
print("Python" <= "Python")
print("java" != "Java")
Output:
True
True
False
True
True
String Length
String Length is referred to the number of characters (including spaces, punctuations, and special characters) it contains. The len() function is used to determine the length of a string in Python.
Example:
# String Length
var_str = "We must learn Python programming language"
# Use the len() function to get the length of a string
var_len = len(var_str)
print(var_len)
print(len("This is my length"))
Output:
41
17
Check String
In Python, we can check if a certain phrase or character is present in a string using inkeyword. The in keyword returns Trueif the search character or phrase is present in the main string, otherwise it will return False.
Other keywords used also include the not in to check if a certain phrase or character is not present in a string.
Example:
# Check String
var_str = "We must learn Python programming language"
# Use the in keyword to check if a certain word, phrase or character is present in a string
var_check = "Python" in var_str
print(var_check)
print("language" in var_str)
print("website" in var_str)
Output:
True
True
False
Use NOT IN Keyword to Check String
To check if a certain phrase or character is not present in a string, we use the not in . This will return True if the characters or the desired word is not present otherwise returns False as a result.
Example:
# Check String
# Use NOT IN Keyword to Check String
var_str = "We must learn Python programming language"
# Use the not in keywords to check if a certain word, phrase or character is not present in a string
var_check = "Python" not in var_str
print(var_check)
print("language" not in var_str)
print("website" not in var_str)
Output:
False
False
True
Use IF and IN Keywords to Check String
We can also use the if and in keywords together to check if a certain phrase or character is present in a string. This will lead us either to execute a block of code if such a decision is True or skip a certain block of code to execute if it becomes False.
Example:
# Check String
# Use IF and IN Keyword to Check String
var_str = "We must learn Python programming language"
var_check = None
# Use the if and in keywords to check if a certain word, phrase or character is present in a string
if "Python" in var_str:
var_check = True
print(var_check, ":" + "The Python word is present in the main text")
if "Java" in var_str:
var_check = True
print(var_check, ":" + "The Java word is present in the main text")
Output:
True :The Python word is present in the main text
Use IF and NOT IN Keywords to Check String
Similar to the above, we can also use the if and not in keywords together to check if a certain phrase or character is not present in a string. This will lead us either to execute or not to execute a block of code depending on the outcome (True or False)
Example:
# Check String
# Use IF and NOT IN Keywords to Check String
var_str = "We must learn Python programming language"
var_check = None
# Use the if and in keywords to check if a certain word, phrase or character is not present in a string
if "Python" not in var_str:
var_check = True
print(var_check, ":" + "The Python word is present in the main text")
if "Java" not in var_str:
var_check = True
print(var_check, ":" + "The Java word is not present in the main text")
Output:
True :The Java word is not present in the main text
Conclusion
In this article, we have explained and demonstrated the Python String. More specifically, we have discussed and practically illustrated several techniques related to how to create and assign value to a Python String, we also showed how to access string items using their index, and how to perform loops in String characters.
Additionally, we also illustrated and explained how to perform various operations on strings such as combining or concatenating Strings, comparing Strings, and last but not least we also showed how to use the len() function to check the length of the string and how to check if certain phrases or characters are present in a string.
All of the above will help you deeply understand the Python String data type and enhance your knowledge of Python. We also recommend learning other data types including the Python numeric data types and general data type practices in Python and other related resources.